Up to Date
 |
 Up to Date |
Homepage |
Datasheets |
Catalog Selector Guide |
Flyers |
Index EmWicon |

Read online
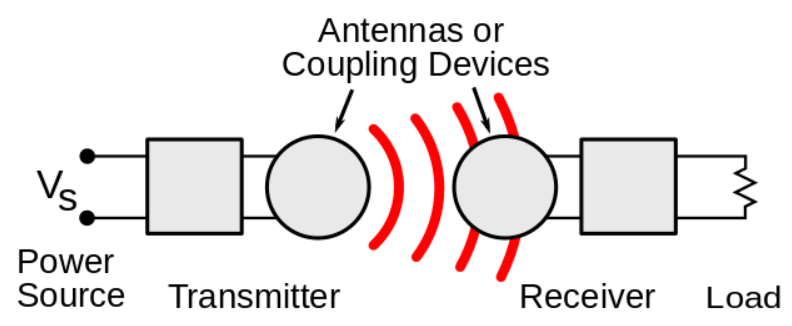
The following article presents the Magnetic Resonance method used by jjPlus for robotics charging with some background information on the various types of wireless power transfer technologies as the supplemental reading so that the decision to implement wireless robotics charging can be made with in-depth domain knowledge. jjPlus has recently finished the development of several wireless power transceiver module pairs with small footprints which are ideal for embedding into robotics products for wireless charging. A transceiver module pair consists of a transmitter module and a receiver module, carefully tuned to be highly resonant with each other in order to accomplish efficient wireless power transfer.

The transmitter module transmits “resonant power” from the surface area of its antenna (coil) defined by X & Y = power area and to a Z =
height which is the distance from the antenna surface. The receiver module, when positioned within the space defined by X, Y and Z, receives
the resonant power and performs the necessary conversions to supply to a load which is typically the battery to be charged.
Key advantages of magnetic resonance wireless power transfer
Merits of embedding resonant wireless charging in robots
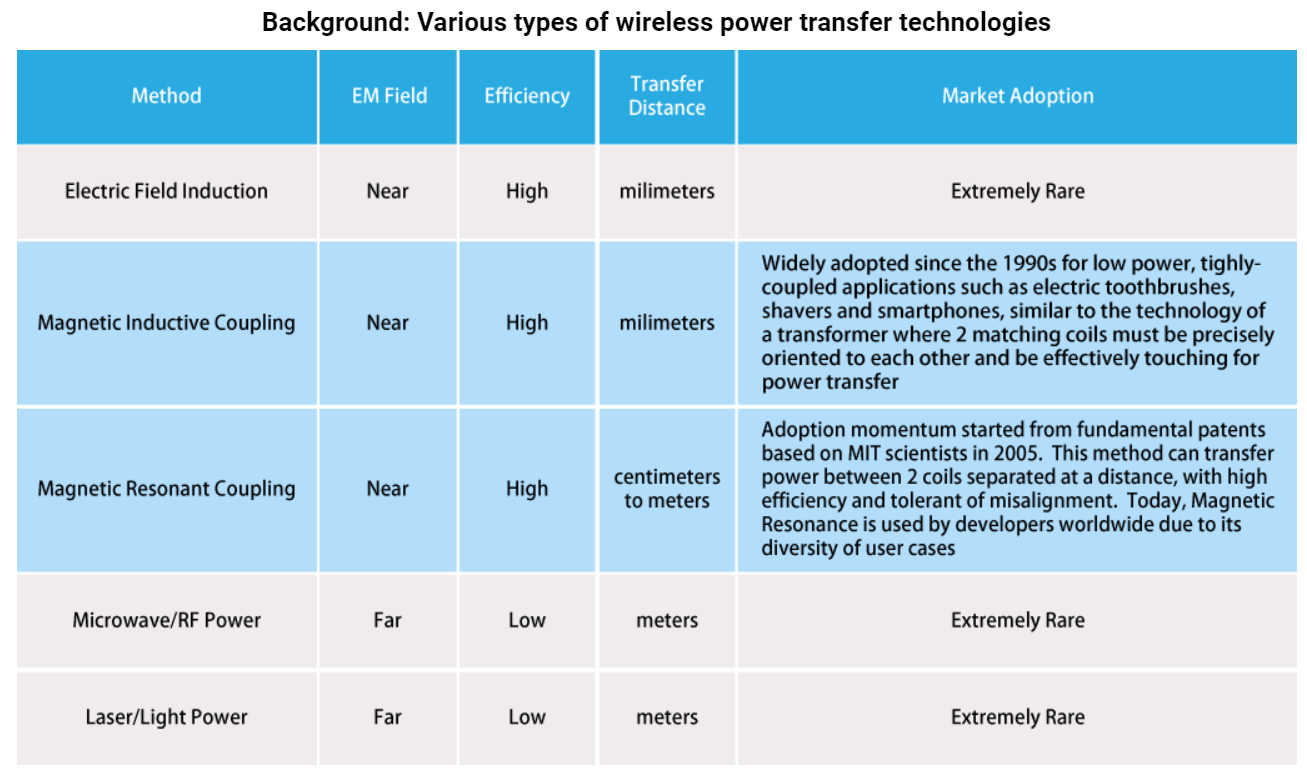
In general, today’s wireless power transfer technologies can be divided into 2 major categories, far field and near field. In far field or
radiative technique, power is transferred by beams of electromagnetic radiation such as Microwave, Radio Frequency, Laser or Light. These
techniques can transfer power over longer distances with advanced beamforming and energy harvesting method but due to the fact that air is a
poor medium for the conduction of power/energy, the environmental loss is large and therefore the transfer efficiency is low. The near
field or non-radiative technique uses either the electricl field or magnetic field to produce capacitive coupling or inductive coupling
respectively in order to achieve wireless power transfer. Its advantage is that high transfer efficiency can be achieved but its weakness is the transfer distance is limited.
The magetic field coupling technique is a much more matured technology over the electric field coupling technique and has been selected by the
developers in the past 2 decades to bring products to mass market with wireless charging. For the 2 types of magnetic field coupling
technique, the Magnetic Inductive Coupling has been widely adopted since the 1990s for charging the batteries of electric toothbrushes and
shavers. Additionally, various types of charging pads and charging stands use the Inductive method (examples are the Qi and PMA standard) to
charge the batteries of today’s mobile devices such as smartphones.
The Magnetic Resonant Coupling technique received great attention in 2005 as the result of the release of research papers and patents from MIT
(Massachusetts Institute of Technology) that took the Magnetic Field Coupling technique to a new height – the ability to deliver wireless power
at a distance with high efficiency by the method of Magnetic Resonant Coupling. jjPlus is an early adoptor of
Magnetic Resonance technology (being a licensee and product realization partner of the
WiTricity Corporation) with a large porfolio of own patents and has been developing wireless power transfer solutions for the past 5 years
including the wireless power solution for the world’s 1st commercially available wireless powered notebook and the world’s 1st AirFuel Resonant certified power transmitter.
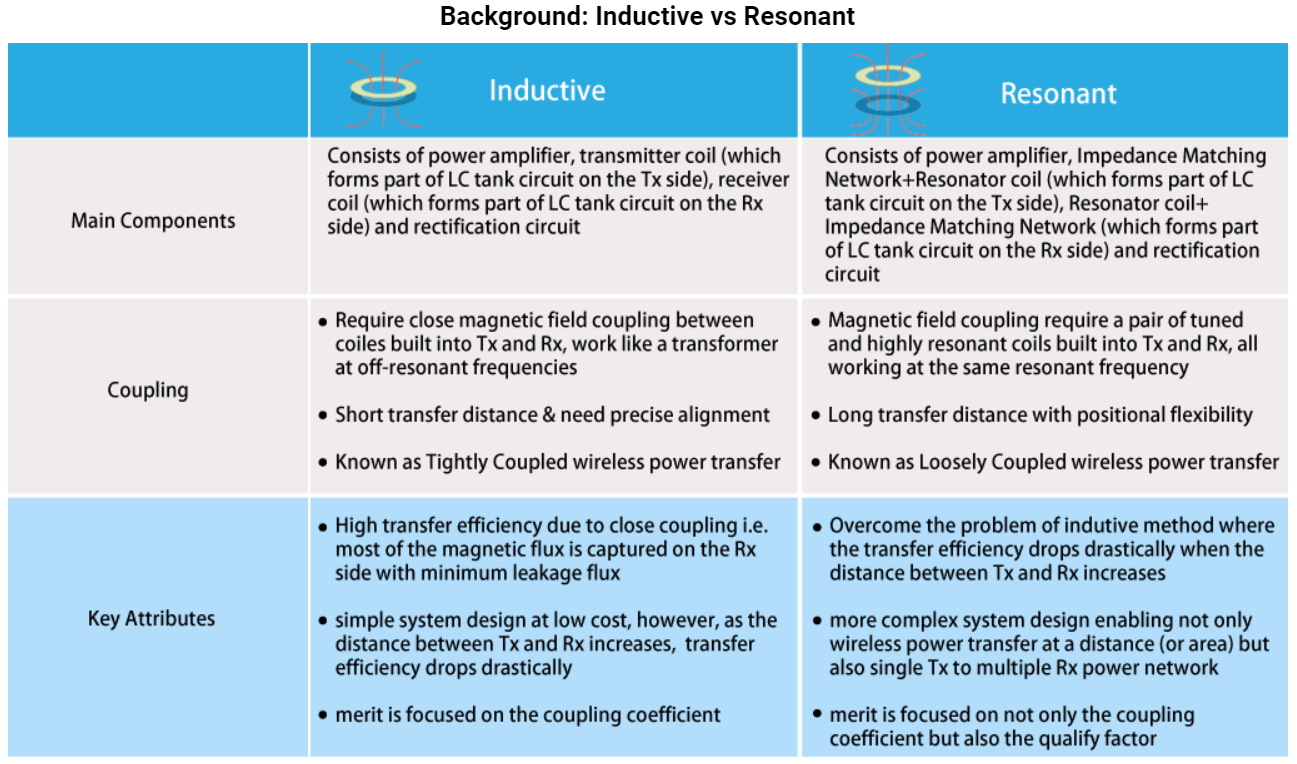
The inductive type wireless power transfer system consists of an amplifier, transmitter coil, receiver coil and rectifying circuit. The transmitter side and the receiver side are electrically isolated by an “air gap”. The system works like an transformer working at off-resonant frequencies where the transmitter antenna (coil) is driven by an AC current generating an alternating magnetic field and this alternating magnetic field will induce an AC current in the nearby receiver antenna (coil) which will then be rectified to supply power to a load. The advantage of Inductive wireless power transfer is it’s low cost, because the system is simple, but as the distance between the transmitter and receiver increases, the power transfer efficiency drops drastically due to reduced magetic coupling.
The resonant type wireless power transfer is the method which has emerged to overcome the drop in efficiency due to the increase in distance between
the transmitter and receiver. It is actually a special case in magnetic induction method where the system works at the same resonant frequency
between the transmitter resonator and the receiver resonator as a pair. It is a more complex system design, however, it not only enables wireless
power transfer at a distance or area, but also multiple device charging or powering with a single transmitter.
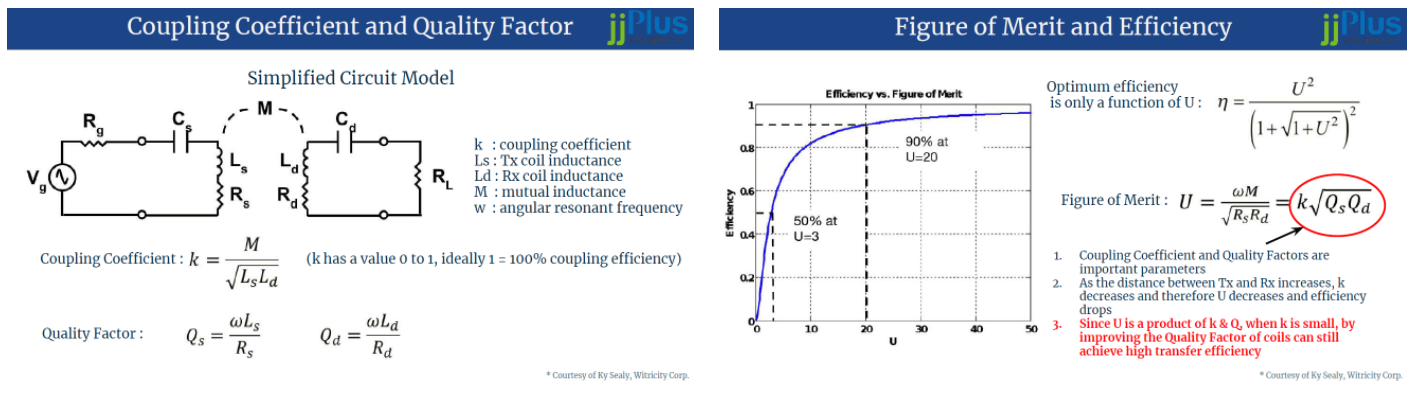
The resonant type wireless power transfer focuses not only on the coupling coefficient K but also on the quality factor Q. The figure of merit of
resonant wireless power transfer efficiency is a product of K and Q. Therefore, when the distance between the transmitter and the receiver
increases causing a small coupling coefficient value, by designing the coils with high quality factor can still overcome the distance issue and achieve high transfer efficiency.